Recent research by ANY.RUN cybersecurity experts has uncovered a cunning attack campaign leveraging a new loader called PhantomLoader to distribute the malicious SSLoad malware. This campaign is particularly concerning because PhantomLoader disguises itself as a legitimate module of the popular 360 Total Security antivirus software, allowing it to bypass traditional security defenses and deliver SSLoad undetected.
The Deceptive Disguise: PhantomLoader
The key element in this attack is PhantomLoader. This cleverly designed loader masquerades as “PatchUp.exe,” a genuine module used by 360 Total Security. This tactic grants it significant advantages:
- Evasion of Detection: By mimicking a trusted program component, PhantomLoader avoids raising suspicion with both security software and the user.
- Pre-execution Advantage: PhantomLoader injects its malicious code before the legitimate software’s main function executes. This suggests a modification of the original module, giving PhantomLoader a head start in the infection process.
- Hidden Payload Extraction: PhantomLoader utilizes XOR decryption to unveil its malicious payload hidden within the legitimate software’s executable file.
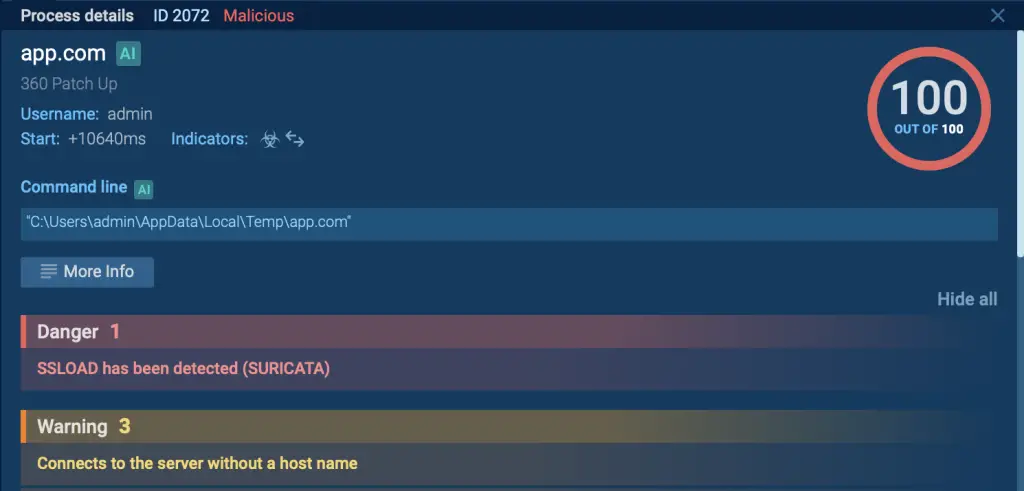
SSLoad malware detection inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
The Multi-Layered Attack Process
The attack unfolds in distinct stages, each designed for maximum stealth:
- Stage 1: Phishing the Initial Infection
- The attack typically begins with a phishing email containing a malicious Office document (often a Word document) as an attachment.
- Once the user opens the document, a macro embedded within the document triggers the infection process. This highlights the importance of user awareness and caution regarding suspicious emails and attachments.
- Stage 2: PhantomLoader Takes Over
- Upon document execution, a new suspicious process named “app.com” launches, indicating the activation of the embedded macro and hinting at malicious activity.
- PhantomLoader, disguised as “PatchUp.exe,” executes before the legitimate software, highlighting the potential vulnerability of compromised modules.
- The loader utilizes XOR decryption to reveal its hidden payload within the legitimate software’s file.
- The decrypted code, equipped with core system functions like memory allocation and DLL loading, facilitates the delivery of SSLoad directly into memory, further enhancing its ability to evade detection.
- Stage 3: SSLoad – The Stealthy Payload
- Once deployed, SSLoad, a Rust-based loader, takes center stage. It employs various techniques to maintain its invisibility:
- Multi-layered String Decryption: SSLoad decrypts its strings in multiple steps, making it difficult for analysis tools to identify its true purpose.
- Mutex Protection: SSLoad utilizes a mutex object to ensure only one instance runs on the infected system, preventing potential conflicts or reinfection attempts.
- System Information Gathering: To adapt its actions to the specific environment, SSLoad gathers crucial details like the operating system version and system architecture.
- Anti-analysis Techniques: SSLoad employs sophisticated measures, including anti-debugging checks, to detect and potentially terminate itself if it senses being monitored by security software.
- Once deployed, SSLoad, a Rust-based loader, takes center stage. It employs various techniques to maintain its invisibility:
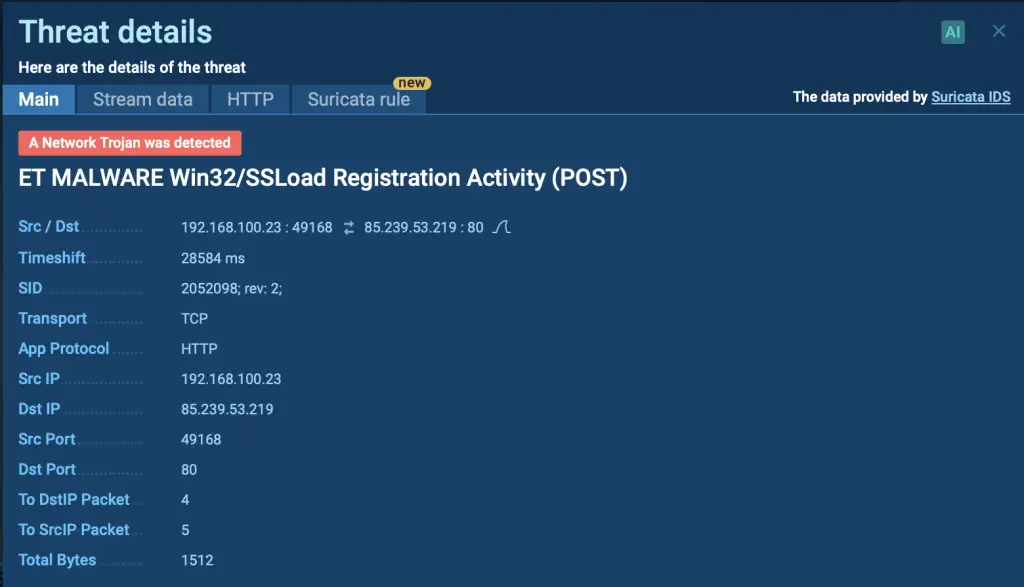
SSLoad malware detected by Suricata rule in ANY.RUN’s sandbox
MITRE ATT&CK Tactics Employed
The ANY.RUN analysis revealed the attackers utilized several tactics outlined in the MITRE ATT&CK framework:
- User Execution (Initial Access): The phishing email with the malicious document serves as the initial access vector, exploiting user interaction.
- Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information (Execution): PhantomLoader utilizes deobfuscation to reveal the hidden code used to load SSLoad into memory, keeping it concealed until the final stage.
- Query Registry (Discovery): SSLoad queries the system registry to gather information about security settings and system configurations.
- System Information Discovery (Discovery): SSLoad actively collects data about the system, including OS details, architecture, and user information, allowing it to tailor its behavior.
- File and Directory Discovery (Discovery): Both PhantomLoader and SSLoad potentially search the system for specific files or directories that could aid in the infection process or help them hide within legitimate processes.
- Data Manipulation (Persistence): SSLoad might modify system data or processes to maintain persistence on the infected system and potentially disrupt normal system functions.
The Importance of Vigilance and Multi-layered Security
This attack campaign highlights the evolving tactics of cybercriminals and underscores the importance of a layered security approach. Here are some key takeaways:
- Phishing Awareness: Educate users about phishing tactics and the dangers of opening suspicious emails and attachments.
- Software Updates: Ensure timely software updates for antivirus and other security applications to patch potential vulnerabilities.
- System Monitoring: Utilize security solutions that monitor system activity and have the ability to detect unusual behavior.
- User Caution: Encourage users to exercise caution when downloading files and visiting unknown websites.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. Summitsystemsissp assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.






