Malicious “Fixes” Lurk Behind Fake Chrome, Word, and OneDrive Errors
Beware of a cunning malware campaign exploiting user trust in familiar software. Hackers are tricking victims into running malicious PowerShell scripts disguised as fixes for fake Google Chrome, Microsoft Word, and OneDrive errors.
Campaign Details:
- Multiple Threat Actors: This campaign involves a coordinated effort by multiple actors, including ClearFake, ClickFix, and TA571 (known for spam and ransomware attacks).
- Social Engineering Tactics: The attacks use website overlays displaying fake error messages that urge users to download and run a “fix” script via PowerShell.
- Varied Delivery Methods: The malicious script can be delivered through:
- Compromised websites with JavaScript overlays
- Booby-trapped HTML attachments resembling Word documents
- Spam emails with malicious links

The ‘ClearFake’ attack chain
Source: Proofpoint
Here’s a breakdown of the different attack chains observed:
1. ClearFake’s Blockchain-Based Delivery:
- Users visit a compromised website that loads a malicious script hosted on the Binance Smart Chain.
- A fake Google Chrome error message appears, prompting the user to install a “root certificate” by copying and running a PowerShell script (as administrator).
- If executed, the script performs various checks and downloads additional payloads, including:
- An information stealer
- Tools to reset the DNS cache and clear clipboard content
- This attack targets users who might trust certificates as part of a secure connection.
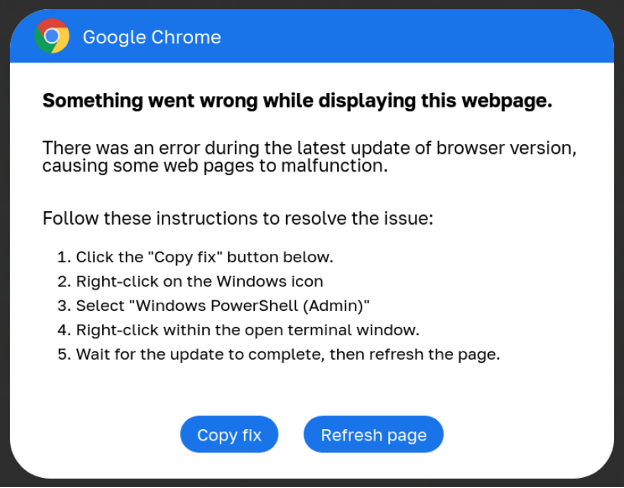
Fake Google Chrome error
Source: Proofpoint
2. ClickFix Injects Fake Errors on Websites:
- Compromised websites are injected with code that creates an iframe overlay displaying a fake Google Chrome error message.
- Users are instructed to open PowerShell (as administrator) and paste a provided script, leading to malware infections.
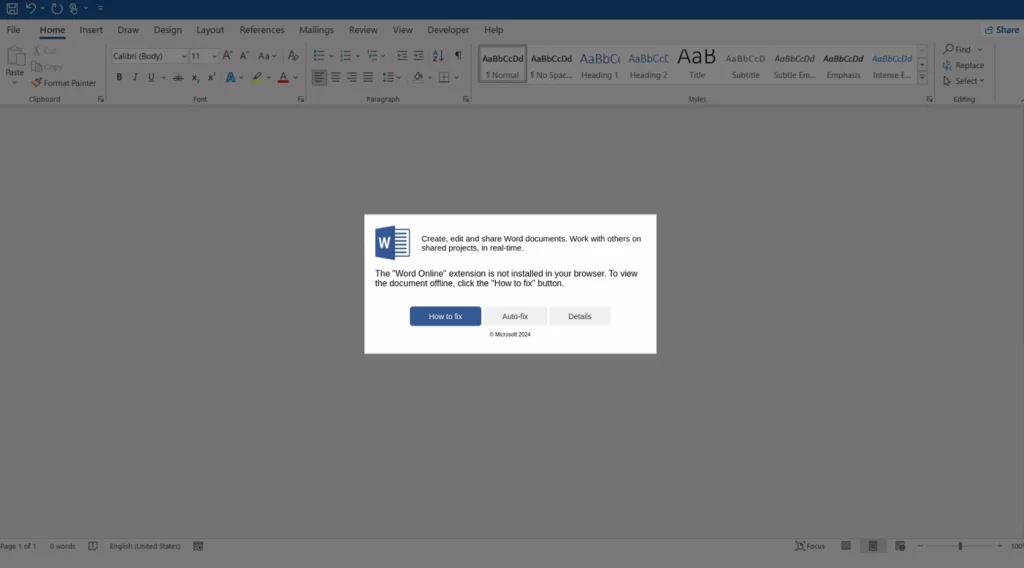
Fake Microsoft Word error leads to malware
Source: Proofpoint
3. Email Phishing with Fake Word Document:
- Emails disguised as containing Word documents arrive with attachments.
- When opened, the attachment displays a fake error message asking users to install the “Word Online” extension to view the document.
- Two “fix” options are offered:
- “How to fix”: copies a base64-encoded PowerShell command to the clipboard for manual execution.
- “Auto-fix”: attempts to download a malicious file (MSI or VBS) disguised as a fix, leading to further infections.
Protecting Yourself:
- Never run scripts from untrusted sources, especially through PowerShell.
- Be wary of unexpected error messages, even from seemingly familiar apps.
- Verify the legitimacy of attachments and website links before opening them.
- Keep your software, including operating system and browser, updated with the latest security patches.
- Consider security solutions that can detect and block malicious PowerShell scripts.
By understanding these tactics, you can avoid falling victim to this deceptive campaign and safeguard your system from malware infections.
Media Disclaimer: This report is based on internal and external research obtained through various means. The information provided is for reference purposes only, and users bear full responsibility for their reliance on it. Summitsystemsissp assumes no liability for the accuracy or consequences of using this information.







